What is Software Architecture and Why is it Important for Developers
In the rapidly evolving landscape of software development, understanding "software architecture" has become increasingly critical for developers and organizations alike. According to the 2022 State of DevOps report by Puppet, high-performing IT teams report up to 60% lower change failure rates, a statistic heavily influenced by the quality of their architectural decisions. Software architecture serves as the foundation upon which applications are built, influencing everything from scalability and performance to maintainability and security. In fact, a poorly designed architecture can lead to increased technical debt, complicating future development efforts and escalating costs.
Furthermore, a recent study by the IEEE reveals that nearly 85% of a software system’s development cost is attributed to downstream maintenance. This underscores the importance of initial architectural planning and the need for developers to prioritize robust software architecture from the outset. With the rise of microservices and cloud-native applications, architects must also consider new challenges and opportunities. As such, investing in effective software architecture not only enhances a development team’s efficiency but also significantly impacts an organization’s overall success in delivering high-quality software products.

Definition of Software Architecture and Its Core Principles
Software architecture is a blueprint for both the system and the project developing it. It encapsulates a set of principles and guidelines that govern software design, ensuring that all components interact effectively. The core principles include scalability, performance, security, and maintainability, guiding developers on how to structure their systems to meet current and future needs.
Tips: Focus on defining the architecture early in the project lifecycle. A clear architecture fosters enhanced communication among team members and streamlines decision-making processes. Regularly revisiting architectural decisions helps to address any emerging challenges as the project evolves.
A well-defined software architecture ensures that applications can adapt to changes in requirements or technology without incurring significant rework. This adaptability is crucial in today’s rapidly changing tech landscape, where new requirements can emerge unexpectedly. Emphasizing abstraction and modularity is key, as it simplifies updates and enhances code readability, making future development more manageable.
Tips: Encourage team collaboration during architectural discussions to capture diverse perspectives. Employing tools like architectural diagrams can help visualize complex interactions and facilitate clearer understanding among stakeholders.
Key Components of Software Architecture and Their Functions
Software architecture serves as the backbone of software development, defining the structure and organization of a system. Key components of software architecture include various modules and interfaces, each with specific functions that contribute to the overall functionality and maintainability of the software. For instance, the separation of concerns allows developers to isolate different functionalities, making it easier to manage complex systems. Additionally, the use of architectural patterns, such as microservices or event-driven architecture, enables teams to achieve scalability and flexibility in their applications.
Recent developments in the field, such as the approach proposed by a research team that leverages pre-trained models, highlight the evolving nature of software architecture. Instead of building models from scratch, developers can "attach" critical components of pre-trained architectures, significantly reducing the time and effort needed for model training. This method demonstrates how architectural design can be revolutionized by innovative strategies, streamlining the process of implementing AI solutions within software applications. Furthermore, tools like Paper2Code exemplify the importance of an efficient architecture that allows seamless translation of research papers into actionable code, addressing the challenges of reproducibility in scientific research.
What is Software Architecture and Why is it Important for Developers
| Key Component | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Modules | Independent units that encapsulate specific functionality. | Enhances maintainability and flexibility of the system. |
| Interfaces | Defined points of interaction between modules or systems. | Facilitates communication and integration of multiple components. |
| Data Management | Structures and processes used to handle data storage and retrieval. | Ensures data integrity and optimal performance. |
| Architecture Patterns | Blueprints that define common practices for structuring systems. | Promotes best practices and reduces complexity in design. |
| Scalability | Ability of the system to handle increased load without performance degradation. | Critical for accommodating growth and user demand. |
| Security | Measures put in place to protect the system from unauthorized access and vulnerabilities. | Essential for safeguarding data and maintaining user trust. |
Importance of Software Architecture in Modern Software Development
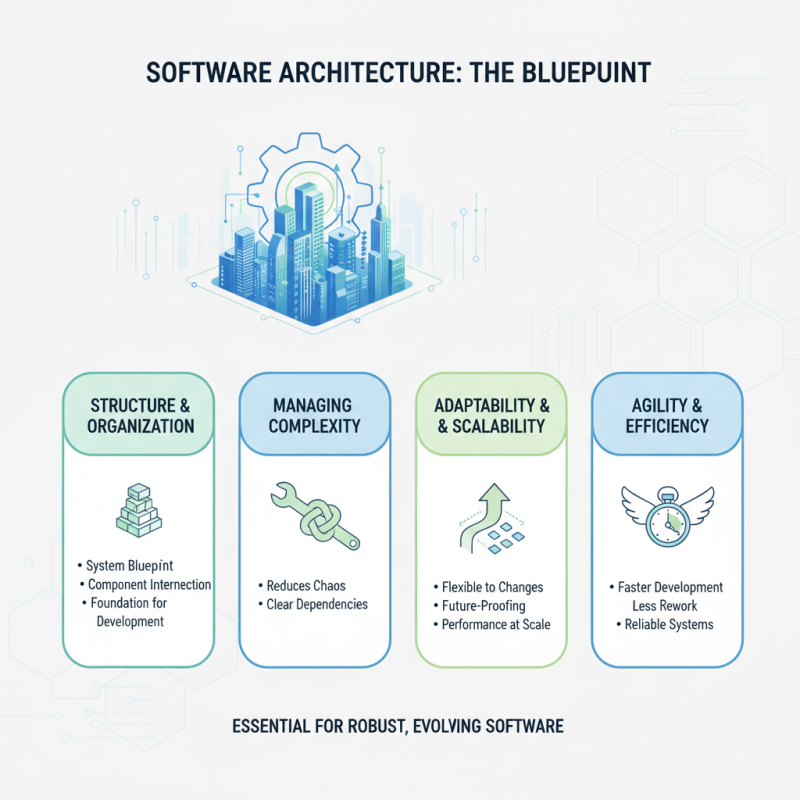
Software architecture is a critical component in modern software development, serving as the blueprint for both the structure and organization of a system. A well-defined architecture helps in managing complexity, ensuring that various components interact seamlessly while maintaining scalability and performance. In today's fast-paced development environment, where agility and flexibility are paramount, robust software architecture allows teams to adapt to changing requirements without significant rework.
Tips: When designing your software architecture, prioritize modularity. This allows for independent development and testing of components, reducing the risk of system-wide failures. Additionally, consider using architectural patterns that best fit your project's needs, such as microservices or event-driven frameworks, to enhance maintainability and deployment efficiency.
Moreover, effective software architecture contributes to better communication among stakeholders. It provides a shared understanding and vision, allowing developers, project managers, and clients to align their goals. By fostering collaboration, teams can identify potential issues early in the development process, leading to more informed decision-making.
Tips: Document your architecture thoroughly. Use diagrams and descriptions to clarify the design and make it accessible for current and future team members. This practice not only aids in onboarding new developers but also serves as a valuable reference throughout the project lifecycle.
Best Practices for Designing Effective Software Architecture
Effective software architecture is crucial for developers as it lays the foundation for building scalable and maintainable systems. One of the best practices in software architecture design is adopting a modular approach. This involves breaking down applications into smaller, manageable components that can be developed, tested, and deployed independently. Such a strategy not only enhances code reusability but also facilitates team collaboration, allowing multiple developers to work on different parts of the application simultaneously.
Another essential practice is ensuring that the architecture can accommodate future growth. With the rise of technologies such as AI and cloud computing, developers must design systems that are flexible and can easily integrate with new tools and frameworks. For instance, the recent open-source release of a development framework for AI applications highlights the need for architectures that support rapid innovation and efficient performance. As businesses increasingly focus on data-driven solutions, prioritizing scalability and adaptability in software architecture becomes key to staying competitive in the digital landscape.
Common Challenges in Software Architecture and How to Overcome Them

Software architecture plays a crucial role in software development, acting as a blueprint that defines the structure and interaction of software components. However, developers often face significant challenges when designing and implementing architecture. One of the common issues is handling complexity, which can arise from numerous interconnected services, especially in the case of microservices. For instance, the transition from a monolithic architecture to a microservices approach can become cumbersome if not approached correctly, complicating deployment and communication between services.
Furthermore, balancing scalability with maintainability presents another challenge. As seen in recent industry trends, companies are increasingly adopting innovative strategies to tackle architectural issues. For example, some organizations have shifted focus from server-side component breakdowns to client-side priorities, enhancing the way systems interact with end-users. By leveraging modern frameworks and methodologies, and fostering collaboration across teams, developers can overcome these challenges, resulting in a robust software architecture that accommodates current and future demands.


